Violent crime is surging in the US, but some argue this is proof the country doesn’t need more police
It’s not just the coronavirus, the social unrest and the soaring temperatures. Violent crime is surging.
Shootings and homicides, which dipped during the initial lockdown phase of the pandemic, are now rising at alarmingly high rates.
But supporters of defunding police — reducing police budgets and redirecting the money to communities in other ways, such as social services — argue this moment is proof that the US doesn’t need more police. They say if cities focused on the root causes of crime, like poverty, substance abuse and disparities in criminal justice, there wouldn’t be as much need for police.
It’s too soon to know for sure why rates of violent crime are spiking, criminologists say. But to make cities safer and earn back the public’s trust, they agree that officials will need to retool police in some capacity — and not by adding more officers.
Why crime is rising
Crime is a symptom of summertime. The combination of heat, no school, outdoor hangouts and interpersonal conflict mean cities often see their highest rates of crime in the warmest months.
But this summer is a different beast.
Richard Rosenfeld, a criminologist who teaches at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, said it’s “reasonably clear” that crime is climbing at least partially due to cities reopening and activities resuming.


Police work a crime scene in Brooklyn where a 1-year-old boy was killed July 13 when gunfire erupted at a family picnic.
His analysis of data for June isn’t complete, but he said the uptick in crime is clear. He said it’s highly likely that widespread social unrest in response to George Floyd’s death and other police violence is contributing to an increase in violent crime.
Rosenfeld believes the protests have stoked existing tensions between police and the communities they serve. When people don’t trust police or fear their response if they call for help, they won’t contact them when crimes occur or cooperate with investigators.
The pandemic, which has disproportionately sickened and killed Black Americans, and the Black Lives Matter protests have hit a raw nerve among people of color, said Richard Aborn, president of the Citizens’ Crime Commission of New York City. This has fueled distrust of institutions, including police, and led to a “crisis of police legitimacy,” he said.
And when people don’t trust the police, Rosenfeld said, they’re more likely to take matters in their own hands and settle disputes on their own.
Defunding police would boost crime rates, some say
Some elected officials say that employing fewer police on the streets would only give criminals a leg up.


People protesting the death of George Floyd and police brutality on June 2 in New York City.
Powerful police unions like the the New York Police Benevolent Association have deflected blame for rising crime and pointed fingers instead at city officials.
When the New York Attorney General issued guidelines for an overhaul of the NYPD, Lynch called them “reheated proposals that have been part of the anti-police agenda for decades.” He also criticized cuts to the NYPD’s budget, and in a statement implied that fewer officers on streets would cause crime to spike.
NYPD Chief of Department Terance Monahan recently said that “anti-police rhetoric” has “basically destroyed morale” among his officers.

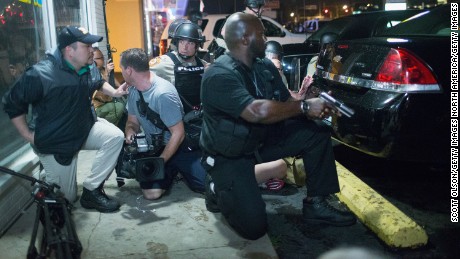
Police take cover as a barrage of gunfire erupts during a demonstration to mark the one-year anniversary of the shooting of Michael Brown on August 9, 2015, in Ferguson, Missouri.
This issue has come up before. In 2014 and 2015, the country saw protests against police brutality and racism after the killings of Michael Brown in Ferguson, Missouri, and Freddie Gray in Baltimore. Some police chiefs argued that their officers didn’t feel comfortable responding to calls out of fear of being vilified and that crime rose as a result — a phenomenon they called the “Ferguson effect.”
Others say a lighter approach to policing will actually make crime go down
A revamped model of policing has already paid off in some cities now considered national models for reform.
Staunch defenders of traditional police tactics are missing an enormous opportunity to reimagine the way law enforcement works, some criminologists say. Reform is essential to regain the public’s trust, they say, which is key to curbing crime.
Lorenzo Boyd, director of the University of New Haven’s Center for Advanced Policing, was a police officer for over 15 years and has trained police for the last two decades. He said policing as it exists now is not sustainable, and those who defend it support a broken system.


An officer in Camden County, New Jersey, grills hot dogs for one of the department’s pop-up neighborhood parties. The city has reformed its police department to focus on de-escalating violence in the community.
Boyd said these people also subscribe to a belief that isn’t logical: That more police leads to less crime.
That’s because the current system of policing in most cities is reactive, not proactive, Boyd said. Officers most often respond to crime after it happens.
“Police as currently instituted do not affect crime rates,” he said. “What they do affect are investigations and arrests after the crime.”
Instead of “cracking down” on crime, police would do better to address some of crime’s root causes, Boyd said. Money could be reinvested from police budgets into social programs that would bolster the communities they police.
Boyd acknowledged this approach is more of a long-term solution than an immediate fix for the country’s recent rise in crime — but he believes it’s a change this moment requires.
“Crime is symptomatic of larger problems in society,” he said. “The reason we have crime is things like homelessness, transiency, levels of addiction, underemployment, undereducation, lack of food, lack of housing — all of those things together make crime something that people will consider. Can we really expect police to address those issues?”
Neither Boyd nor Aborn, who leads the Citizens’ Crime Commission, believe cities should defund the police entirely. Instead, they said departments should emphasize deescalation and empathy — skills they can build by learning from the communities they serve.
Rosenfeld, the criminologist, disagrees with those who argue the country can’t reform police and respond effectively to the surge in violence at the same time.
“We have to do both,” he said.
The health and security of the nation — this summer and beyond — may depend on it.
![]()


