Myth that kids can’t get badly ill from Covid is further debunked
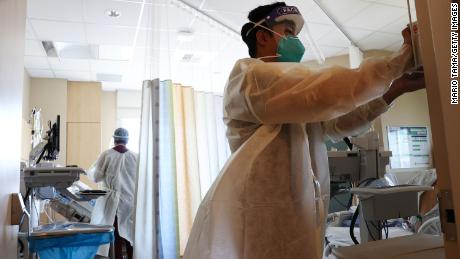
That’s a 21.4% increase from the previous week in the number of new children getting hospitalized every day with Covid-19.
“This virus that we’re dealing with now is a game changer,” Kline said Monday. “It’s just so easily transmitted from person-to-person.”
Doctors say it’s crucial to protect children against the now-dominant Delta variant — not just to preserve in-person learning and protect children’s health, but also to help prevent even more aggressive variants from emerging.
Almost half of children hospitalized with Covid-19 had no known underlying condition
The weekly count of children newly infected with Covid-19 has more than doubled in two weeks.
About 39,000 new cases were reported during the week ending July 21, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.
That number soared to 94,000 new cases during the week ending August 5, the AAP said.
With the rise in both new cases and hospitalizations, it’s not just children with preexisting conditions getting hospitalized.
Covid-19 deaths in children shouldn’t be ignored, CDC chief says
While children are far less likely to die from Covid-19 than adults, the deaths are still significant, CDC Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky said.
The main reason why Covid-19 is deadlier for children than other infectious diseases is because many children are vaccinated against other diseases, said Dr. James Campbell, professor of pediatrics at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
“Nobody’s dying of polio, nobody’s dying of measles in the United States. Nobody’s dying of diphtheria,” Campbell told CNN last month.
And it could be several more months before a vaccine is authorized for children under age 12.
Rebecca Calloway’s 7-year-old daughter Georgia is one of thousands of young children testing various doses of Covid-19 vaccines to make sure they’re safe and effective before they get authorized.
While childhood deaths from Covid-19 and Type 1 diabetes are rare, “You don’t want to be that statistic,” Calloway said.
Protecting kids from Covid-19 is critical to keep them in schools
“Our children deserve to have full-time, in person, safe learning with prevention measures in place. And that includes masking for everyone in schools,” Walensky said.
Some students are returning to schools for the first time in a year. But long-awaited classroom learning can be quickly derailed by an infection or outbreak.
And it doesn’t take much for Covid-19 to shut down a school again. Even one case can have a ripple effect on students, faculty and staff.
“We need adults to run schools, and if my adults are sick or needing to quarantine, I don’t have adults present to provide the education,” said Carlee Simon, superintendent of Alachua County Public Schools in Florida.
The school board voted to require face masks for the first two weeks of school, but Florida’s governor has threatened to reduce funding to schools that require masks.
And that has the superintendent worried.
“When we have families that don’t want to have masks on their child, what they’re doing is not only making the higher chance they will have to be quarantined,” Simon said.
If a student gets infected, “they will also have other students who did have masks on who would also need to be quarantined.”
“Everybody wants to move forward. Nobody wants to have masks forever,” Simon said. But “we would like to be able to be safe and have instructional time with our students.”
In addition to masks in schools, the CDC recommends layering other strategies such as improved ventilation, physical distancing and testing on a screening basis.
MIS-C and long Covid can leave lasting impacts
All pediatric patients who tested positive should have at least one follow-up exam with a pediatrician, the AAP said.
Children who had moderate or severe Covid-19 may be at greater risk for subsequent heart disease, the pediatrician group said.
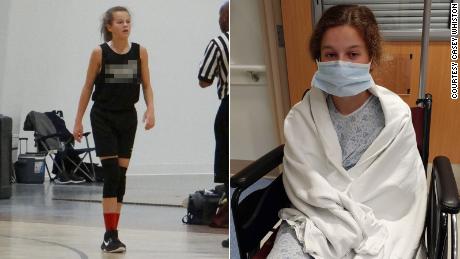
In some cases, children who start with mild or even no symptoms from Covid-19 end up hospitalized weeks or months later with a condition called MIS-C — multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
It happens when “the virus induces your body to make an immune response against your own blood vessels” — which can cause inflammation of the blood vessels, said pediatrician Dr. Paul Offit, director of the Vaccine Education Center at the Children’s Hospital in Philadelphia.
Often, children with MIS-C don’t start off very sick with Covid-19.
“Usually children are picked up incidentally as having (coronavirus). Someone in the family was infected, a friend was infected, so they got a PCR test. And they’re found to be positive. … Then they’re fine,” Offit told CNN.
“Then a month goes by, and they develop a high fever. And evidence of lung, liver, kidney or heart damage. That’s when they come to our hospital.”
It said 99% of MIS-C patients had tested positive for coronavirus, and the other 1% had contact with someone with Covid-19.
The median age of patients with MIS-C was 9 years old.
“CDC is working to learn more about why some children and adolescents develop MIS-C after having COVID-19 or contact with someone with COVID-19, while others do not,” the CDC says.
“Based on what we know now about MIS-C, the best way you can protect your child is by taking everyday actions to prevent your child and the entire household from getting the virus that causes COVID-19.”
The best steps parents can take to protect their children include getting vaccinated and vaccinating children ages 12 and up, Walensky said.
And even if a parent is fully vaccinated, there’s a small chance they could catch an asymptomatic breakthrough infection and pass the virus to their children.
That’s why it’s a good idea for all parents of young children to wear masks in public.
But the best way to protect unvaccinated children, Walensky said, “is to surround them with vaccinated people.”
Children can accidentally help spur new variants
Protecting children from getting Covid-19 can help everyone in the long run, doctors say.
“That’s, of course, the concern,” Walensky said.
“If we are going to continue to allow this virus to spread, we’re going to continue to allow these variants to be created,” he said.
“We’re not going to be able to stop this pandemic until we have a significant percentage of the population vaccinated.”
CNN’s Deidre McPhillips and Jen Christensen contributed to this report.
![]()